Low volume manufacturing

Introduction
In today's ever-changing manufacturing landscape, Low Volume Manufacturing (LVM) plays a crucial role in how industries produce goods. This article explores the concept of LVM, highlighting its significance and the various advantages it offers. Understanding LVM, from its definition to the types of products it suits and when to use it, is essential for manufacturers aiming to excel in a competitive market.
What is Low Volume Manufacturing?
Low-volume manufacturing, often referred to as LVM is a production approach characterized by the creation of limited quantities of a product. Unlike high-volume manufacturing, which produces large quantities of items in a continuous and repetitive manner, LVM focuses on producing smaller batches tailored to specific demands. This method aims to find a balance between cost-effectiveness and customization, providing manufacturers with a strategic advantage in certain situations.
Why Low-Volume Manufacturing Matters
The significance of LVM goes beyond operational convenience; it lies in its ability to adapt and respond in manufacturing environments. In an era where consumer preferences change rapidly, and niche markets become significant sources of revenue, LVM offers flexibility. By allowing quick adjustments in production volume, LVM enables manufacturers to adapt swiftly to market shifts, minimize excess inventory, and optimize resource allocation.
Understanding Low-Volume Manufacturing
Defining Low-Volume Manufacturing
At its core, LVM embodies a philosophy of "less is more." It's a manufacturing strategy finely tuned to balance precision and adaptability. Instead of drowning in the vastness of mass production, LVM thrives in the realm of focused, customized production. This approach excels in delivering niche, high-quality products without excessive waste or undue risk.
Types of Products Suited for Low-Volume Manufacturing:
LVM is not a one-size-fits-all solution; it excels in specific niches:
- Prototypes: LVM is ideal for prototyping new products, allowing manufacturers to test and refine designs without committing to large-scale production.
- Customized Goods: Products requiring personalization, like custom-made furniture or bespoke jewelry, are well-suited for LVM. It enables artisans to craft items tailored to individual tastes.
- Limited-Edition Items: Luxury brands often use LVM to create limited-edition runs, maintaining exclusivity and prestige.
Advantages of Low-Volume Manufacturing:
- Cost Efficiency: LVM is highly cost-efficient for small-scale productions, minimizing material wastage and overhead costs, ensuring meticulous attention to each product, and reducing unnecessary expenses.
- Customization: Unlike mass production, LVM embraces customization, allowing manufacturers to tailor products to unique customer requirements, fostering brand loyalty and niche market penetration.
- Reduced Risk: By producing smaller batches, LVM mitigates risks associated with manufacturing errors or market changes, enabling quick adaptation without significant losses.
When to Consider Low-Volume Manufacturing:
Strategically employing LVM requires a keen understanding of market dynamics. Consider LVM when:
- Market Volatility: In sectors prone to rapid shifts in consumer preferences, LVM offers agility, enabling swift adaptation to market fluctuations without excess inventory.
- Customization is Essential: If your product's success depends on meeting individual customer requirements, LVM is a valuable option, allowing the delivery of unique, customer-centric solutions.
- Prototyping and Testing: When embarking on a new product venture, LVM facilitates prototyping and testing phases, reducing financial risks associated with full-scale production.

Benefits of Low-Volume Manufacturing
Cost-Effective Production
Low-volume manufacturing (LVM) excels in cost-effective production. By tailoring the manufacturing process to specific, limited quantities, businesses can significantly reduce operational costs. LVM focuses on precision and efficiency, avoiding overproduction, excessive resource use, and waste. Each unit in LVM receives meticulous attention, ensuring optimal resource allocation and minimal wastage. This makes LVM a financially savvy strategy, especially suitable for industries where economies of scale are not the primary driver.
Reduced Inventory Costs
Inventory costs can quietly drain resources in manufacturing. LVM addresses this issue effectively. By producing goods in smaller, manageable batches, LVM reduces the need for extensive warehousing and storage facilities. Excess inventory, often a concern in traditional mass production, is minimized or eliminated. This leaner approach not only lowers storage costs but also mitigates risks related to unsold, obsolete stock. As a result, LVM helps businesses maintain better control over their finances, directing resources where needed.
Faster Time to Market
In the competitive race to seize market opportunities and respond to swiftly changing consumer preferences, speed is crucial. LVM's streamlined production approach provides a distinct advantage: a faster time to market. The agility of LVM enables manufacturers to respond quickly to market demands. Design changes, modifications, and improvements can be swiftly integrated into the production process, without the delays typical of large-scale manufacturing. This allows businesses to introduce their products to consumers more rapidly, gaining a competitive edge in a dynamic marketplace.
Challenges in Low-Volume Manufacturing
Quality Control and Consistency
While LVM offers numerous advantages, it presents challenges in maintaining quality control and consistency. Mass production relies on standardized processes and machinery for uniformity, but LVM's customized approach introduces complexities that require vigilant oversight. Manufacturers must invest in stringent quality control measures to ensure that each product meets exacting standards. Failure to do so could result in variations and defects that harm the brand's reputation and customer satisfaction.
Supplier Selection and Management
Effective LVM depends on a network of suppliers capable of handling the specific demands of this production methodology. Selecting and managing suppliers adept at managing lower volume orders can be challenging. Manufacturers must assess the reliability, scalability, and flexibility of their suppliers. Furthermore, building strong communication and collaboration with suppliers is crucial to consistently meet production timelines. Striking the right balance between cost efficiency and supplier performance is a delicate balancing act in LVM.
Scalability Concerns
As businesses grow and market demand changes, scalability becomes a concern. While LVM is highly effective for small to medium-sized production runs, transitioning seamlessly to mass production can be a challenge. Manufacturers must carefully plan for scalability to avoid bottlenecks and disruptions as production volumes increase. This involves reevaluating processes, infrastructure, and supply chain arrangements to ensure a smooth transition from LVM to higher production scales.
Low-volume manufacturing offers compelling benefits for businesses in terms of cost-effective production, reduced inventory costs, and faster time to market. However, it's crucial to address challenges related to quality control, supplier management, and scalability to fully realize the potential of LVM as a strategic manufacturing approach. Careful navigation of these challenges can empower businesses to leverage the advantages of LVM while minimizing potential pitfalls.

Choosing the Right Manufacturing Process
Injection Molding for Low-volume Production
Injection molding, known for its efficiency in high-volume manufacturing, also has a place in low-volume production. This process involves injecting molten material into a mold cavity, allowing it to cool and solidify, resulting in precise, repeatable parts. While tooling costs can be substantial, making it less suitable for ultra-small runs, injection molding excels when producing hundreds to thousands of units. Its ability to maintain consistent quality and offer cost-effective unit prices makes it a smart choice for the right production scale.
CNC Machining for Custom Parts
When customization is essential, Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is the tool of choice. This subtractive manufacturing process involves precision machining of materials using computer-controlled tools. CNC machining is versatile and capable of crafting intricate, one-of-a-kind parts with impeccable precision. While it may not be the most cost-effective option for high-volume runs, its flexibility and suitability for small batches make it ideal for projects requiring unparalleled accuracy and customization.
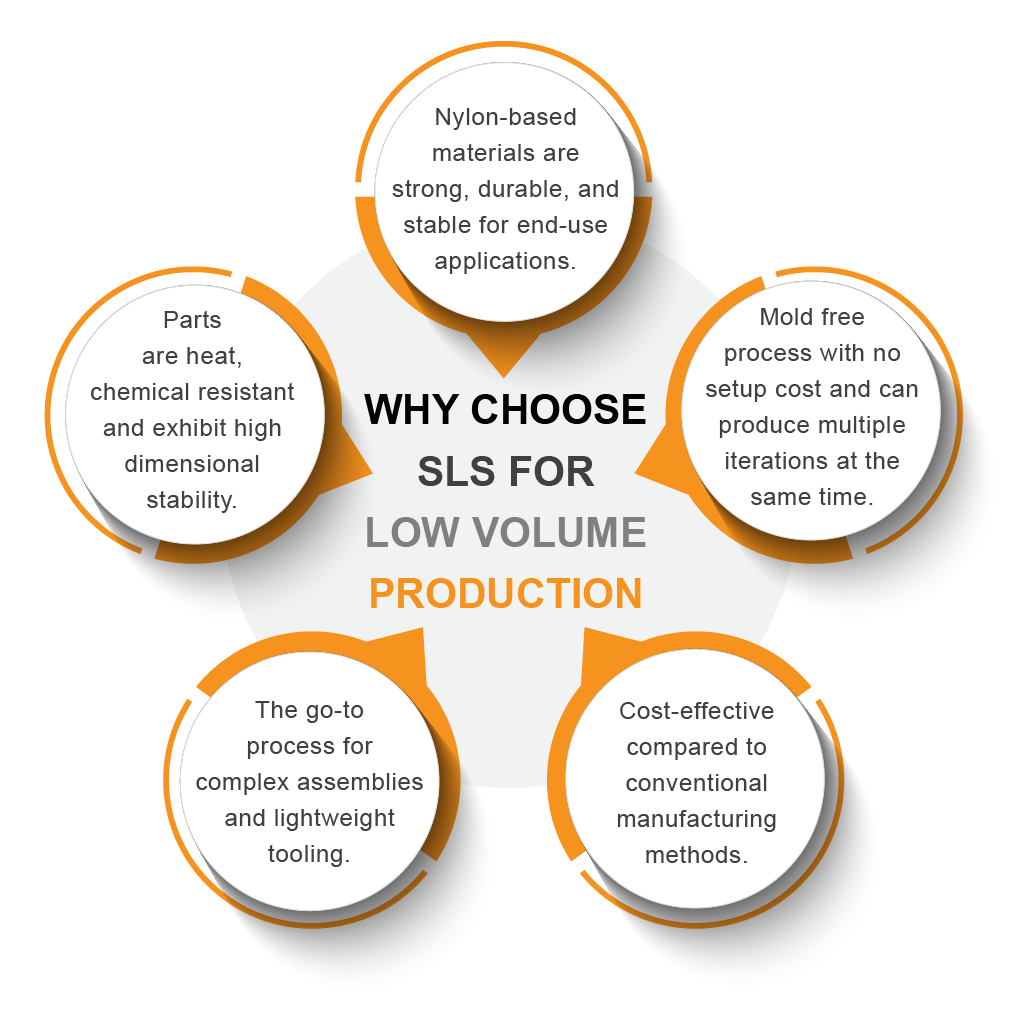
3D Printing and Rapid Prototyping
In the realm of rapid prototyping and low-volume production, 3D printing is a technological marvel. This additive manufacturing process constructs objects layer by layer from digital designs. While it excels at producing prototypes quickly, its capabilities have expanded to include short-run production. 3D printing offers design freedom, allowing for complex geometries and rapid design iterations. However, it may not match traditional manufacturing methods in terms of speed and cost-effectiveness for large-scale production.
Sheet Metal Fabrication for Small Batches
Sheet metal fabrication, rooted in traditional craftsmanship, is a reliable choice for producing small batches of precision components. This process involves cutting, bending, and assembling metal sheets to create various products. Its ability to cater to low-volume orders without exorbitant tooling costs positions sheet metal fabrication as an economical choice for projects requiring durability, strength, and intricate designs.
Making Informed Decisions for Your Production Needs
Entering the realm of low-volume manufacturing requires careful consideration. To fully harness its potential, businesses must make informed decisions. This journey begins with a meticulous evaluation of manufacturing partners to ensure they align with your vision and requirements. Asking the right questions and scrutinizing their capabilities are crucial. Establishing a long-term relationship based on trust and transparency is the foundation of sustained success in low-volume manufacturing.
Managing Costs in Low-Volume Manufacturing
Material Selection for Cost Efficiency
Material selection is crucial for cost efficiency in low-volume manufacturing. Choosing readily available materials with established supply chains can reduce production costs. Additionally, evaluating material properties and their suitability for the intended purpose helps prevent over-specification and unnecessary expenses.
Optimizing Production Processes
Streamlining production processes is essential for cost management in low-volume manufacturing. Continuously evaluating and refining manufacturing workflows can lead to reduced labor costs, shorter lead times, and improved resource allocation. Automation and lean manufacturing principles can enhance efficiency and minimize wastage, driving down production expenses.
Economies of Scale vs. Low-Volume Production
The balance between economies of scale and low-volume production is a persistent challenge. Mass production often enjoys cost advantages due to bulk purchasing and standardized processes, while low-volume production offers flexibility and responsiveness to market demands. Choosing the right approach involves assessing project requirements, market dynamics, and long-term goals. A hybrid strategy that combines both approaches may be the most prudent solution in some cases.
Absolutely, choosing the right manufacturing process and cost management strategies are key factors in the success of low-volume manufacturing. It's important to thoroughly assess your project's requirements, budget constraints, and long-term goals to make an informed decision about which manufacturing method to use. Additionally, continuously optimizing production processes and material selection can help control costs and ensure that you deliver high-quality products that meet customer expectations. By finding the right balance between cost-efficiency and product quality, manufacturers can thrive in low-volume production and remain competitive in the market.
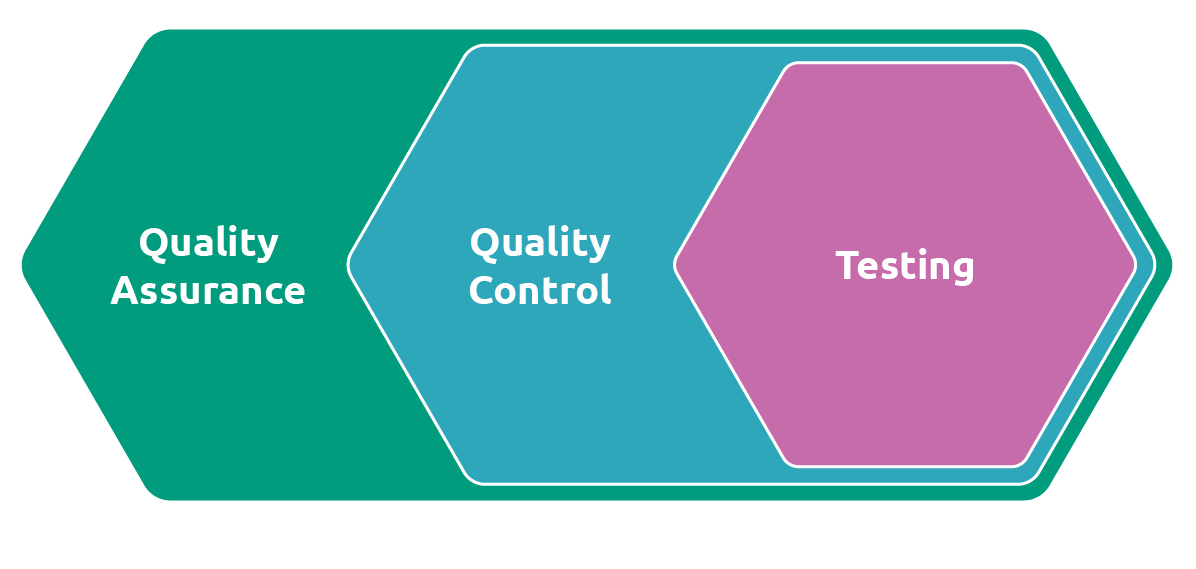
Quality Assurance and Testing
Implementing Quality Control Measures
Quality control is a crucial aspect of maintaining product integrity. It involves a meticulous process, starting with raw material inspection and ending with final product assessment. Statistical process control techniques, Six Sigma, and Total Quality Management principles help detect anomalies early and prevent defects.
Inspection and Testing Protocols
Robust inspection and testing protocols are essential to ensure product quality. Non-destructive testing methods like ultrasonic or radiographic inspection can uncover hidden flaws, while functional testing simulates real-world conditions to assess product reliability.
Continuous Improvement Strategies
Quality assurance is a dynamic philosophy that requires continuous improvement. Embracing Kaizen principles and regularly reviewing processes, collecting feedback, and analyzing post-production data can lead to product refinement and higher quality standards over time.
By carefully managing costs, selecting the right manufacturing process, and implementing effective quality assurance measures, manufacturers can excel in low-volume manufacturing while delivering high-quality products that meet customer expectations.
Finding the Right Manufacturing Partner
In the complex world of manufacturing, choosing a manufacturing partner is a crucial decision that can shape a business's success. This section explains how to find the ideal manufacturing partner.
Evaluating Manufacturing Partners
Selecting a manufacturing partner is like forming a strategic alliance. The evaluation process starts by looking into the partner's abilities, including their technical skills, production capacity, and quality control methods. A partner's track record and reputation in the industry provide valuable insights into their reliability and commitment to quality. Additionally, checking if they follow industry certifications and standards is essential.
Questions to Ask Potential Manufacturers
The key to making the right choice is asking the right questions. Potential manufacturers should be thoroughly questioned, covering areas like production times, flexibility in handling order changes, and plans for unexpected issues. Inquiring about their quality control approach and willingness to work on product improvements is equally important. By examining their answers, manufacturers can understand how well a potential partner aligns with their goals.
Building a Long-Term Relationship
In manufacturing, short-term partnerships usually don't yield the best results. Long-term success comes from building a lasting relationship with a manufacturing partner. Clear communication and trust are the foundation of such a relationship. Being clear about expectations, pricing, and quality standards paves the way for a productive collaboration. Nurturing this partnership is like tending to a delicate ecosystem, ensuring a consistent flow of high-quality products and lasting business prosperity.
Quality Assurance and Testing
Quality assurance and testing are fundamental to manufacturing excellence. They require strict control measures, thorough inspection, and a strong commitment to continuous improvement. At the same time, finding the right manufacturing partner is a strategic process that involves careful evaluation, insightful questioning, and building a long-term relationship based on trust and shared goals. By combining these two aspects, manufacturers can achieve unparalleled success and product excellence in today's complex manufacturing landscape.

Conclusion
As we conclude this exploration of low-volume manufacturing, it's clear that this production approach plays a crucial role in modern industry. It's a dynamic and adaptable strategy that allows businesses to navigate today's complex markets effectively. In this conclusion, we summarize the key points and stress the importance of making informed decisions to unlock the full potential of low-volume manufacturing.
The Role of Low-Volume Manufacturing in Modern Industry
Low-volume manufacturing is a vital part of modern industry, providing a strategic alternative to traditional mass production. It excels in situations where customization, flexibility, and responsiveness are essential. Producing smaller batches of high-quality products empowers businesses to meet specific demands, adapt to market changes, and reduce excess inventory. In a constantly changing world with evolving consumer preferences, low-volume manufacturing offers versatility and efficiency.
In summary, low-volume manufacturing is the solution to modern industry's evolving needs. It drives innovation, flexibility, and efficiency. By choosing the right manufacturing partners, asking the right questions, and nurturing long-term relationships, businesses can unlock the full potential of low-volume manufacturing. In an ever-changing world, it serves as a compass guiding industry toward excellence and sustainability.

